Types of Rainfall
The water that comes back to the surface of the earth in its various forms like rain, snow, hail, etc. is called precipitation. Rain is one type of precipitation. When precipitation occurs in the form of water is known as rainfall. A major part of the precipitation occurs in the form of rain and a minor part of the precipitation occurs in the form of snow. Other forms of precipitation such as hail, sleet, mist, are very small and generally ignored. Depending on the different atmospheric conditions, rainfall may be of the following types:

1. Cyclonic Rainfall
This type of rainfall is caused by the difference of pressure within the air mass on the earth’s surface. If low pressure is generated somewhere, warm moist air rushes with violent forces from the adjacent area to the low-pressure zone.
The heated moist air rises up with the circular motion and gets condensed at the higher altitude, and finally, heavy rainfall occurs.
Cyclonic rainfall is classified into the following two categories:
i. Frontal type: Front is a boundary joining warm moist air mass resulting in the precipitation of the moist air mass.
ii. Non-frontal type: In this cold air mass moves whereas moist air mass is stationary.
2. Frontal Rainfall
Frontal rainfall is a type of cyclonic rainfall. When the moving warm moist air mass is blocked by the zone of the cold air mass, the warm moist air rises up (as it is lighter than cold air mass) to a higher altitude where it gets cooled adiabatically to form a cloud and ultimately heavy rainfall occurs.
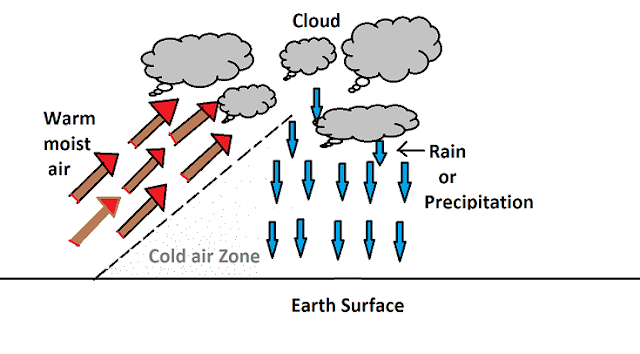
3. Non-frontal rainfall
Non-frontal rainfall is also a kind of cyclonic rainfall. When a mass of warm moist air rushes from the surrounding zone to the lower pressure zone, a pocket is formed, and the warm moist air rises to a higher altitude like a chimney.

At higher altitudes, it gets cooled adiabatically to form a cloud. Rainfall caused by such clouds is known as non-frontal rainfall.
4. Convective Rainfall
In tropical countries, when the ground surface is unevenly heated, especially on hot days, warm air rises to high altitudes and cold air takes its place with high velocity.

Thus, at high altitude, the warm, moist air mass condenses and causes heavy rainfall. This is called convective rainfall.
5. Orographic Rainfall
When the moving warm moist air is barred by some mountain, then it rises up to a high altitude along the mountain slope.

At the high altitude, it gets condensed and heavy rainfall occurs. This type of rainfall is called orographic rainfall.
Read Also: