Coning of Wheels
The art of providing an outward slope of 1 in 20 to the treads of wheels of rolling stock is known as the coning of wheels.
The coning of wheels is provided to keep the vehicle in the central position with respect to the track and helps the vehicle to move smoothly on the straight and curved track.
In the case of a straight and level track (which is shown in Figure 1), the flanges of the wheels have an equal perimeter.
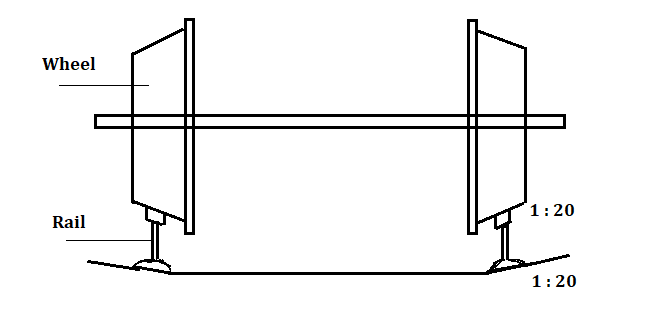
But in the case of a curved track, the situation will be different as shown in Figure 2. In this situation, the outer rail has to cover a greater distance than that of the inner rail. Also, due to the action of centrifugal force on a curve, the vehicle has a tendency to move out towards the outer rail.
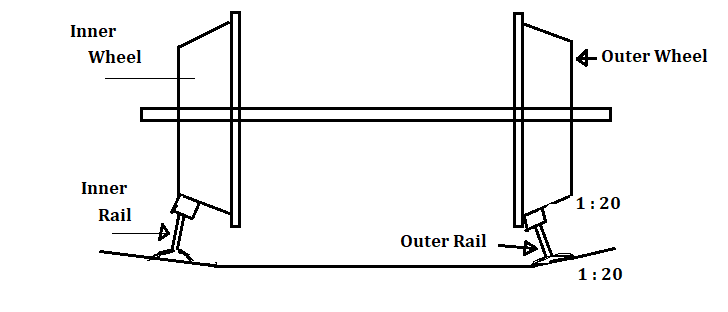
To overcome this, the circumference of the flange of outer wheel is made greater than that of the inner wheel and this helps the outer wheel to travel a longer distance than the inner wheel.
The object of Providing Coning of Wheels
Coning of wheels is done to achieve the following object:
1. To reduce the wear and tear of the wheel flanges and rails.
2. To prevent lateral movement of trains.
3. To prevent the wheels from slipping to some extent.
Read more: