What is a Dummy Activity?
- A dummy activity is an imaginary activity.
- It is represented by the dashed arrow.
- Does not consume any time and resources.
Example of Dummy Activity

Purpose of Dummy Activity
There are two reasons to use dummy activity one is grammatical purpose another one is logical purpose.
1. Grammatical Purpose
We will try to understand it by seeing the picture. The activity ‘A’ starts from node 1, and B also starts from node 1, and both activities end at node 2.
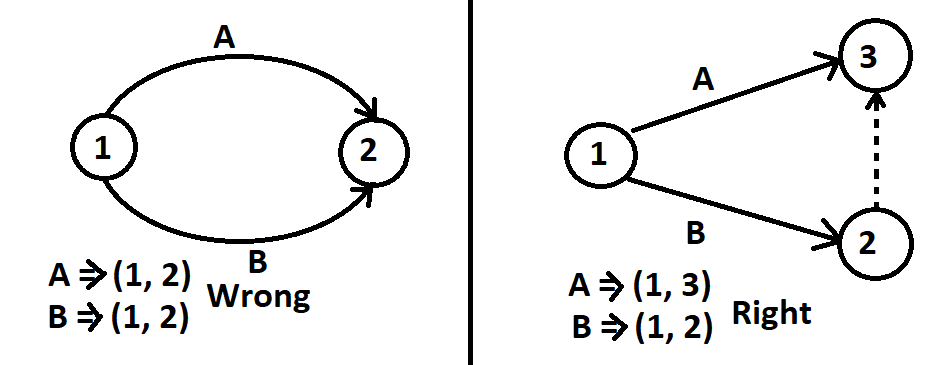
We can represent it as follows:
- A ⇒(1,2)
- B ⇒(1,2)
Now you can see that both identities are the same, so they lose their identity. Here, the main logic is that they both start at the same time and also finish at the same time. To find out their identity with logic, we used a dummy activity as fig.2
Now we can represent like as
A ⇒(1, 3)
B ⇒(1, 2)
2. Logical Purpose
You can not provide the same activity twice in your network diagram.
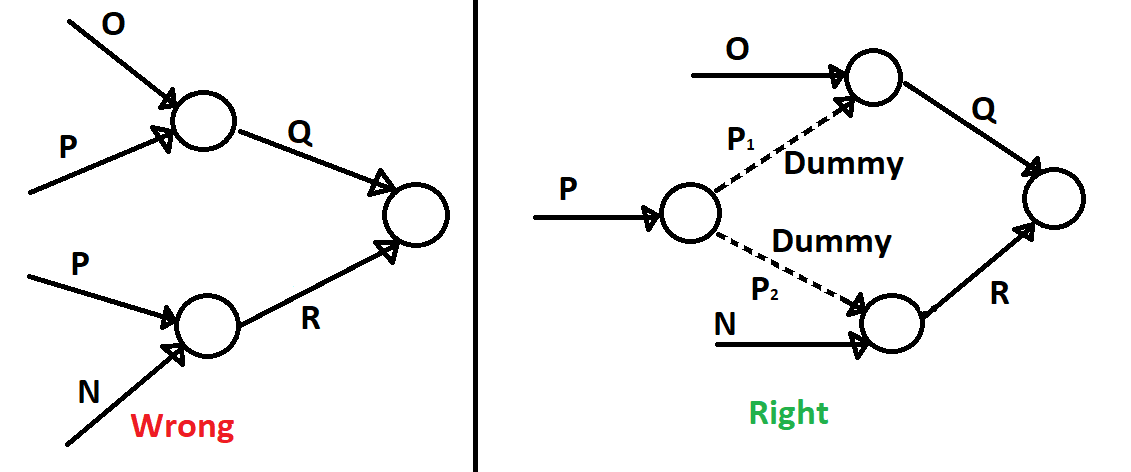
In the above picture, it shows that the P activity is two times in a single network diagram. So to avoid these types of errors in the network diagram, we provide a dummy activity.
Rules for Removing Redundant Dummy Activity
You can use as many dummy as you wish, but sometimes it asks to remove dummy which is not required. Five golden rules are used for removing redundant dummy.
Rule: 1
If the dummy originated from one node.
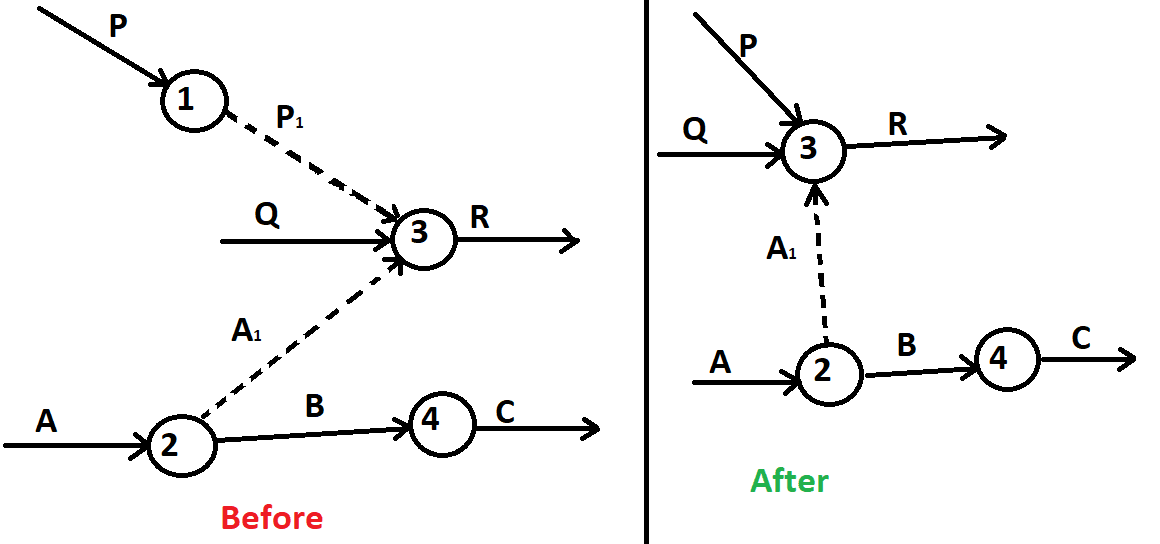
Here, the P1 dummy is not required
Rule: 2
If a dummy is the only arrow going into a node.
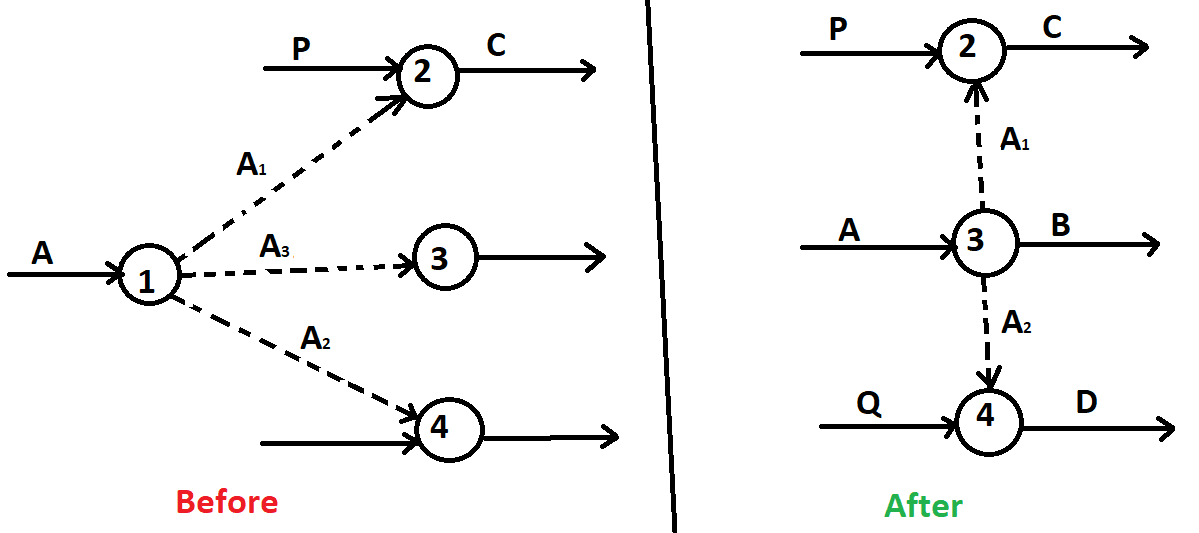
Here, A3 dummy is not required
Rule: 3
If two activities have set of a predecessor.
Rule: 4
If two activities have the same set of a successor.
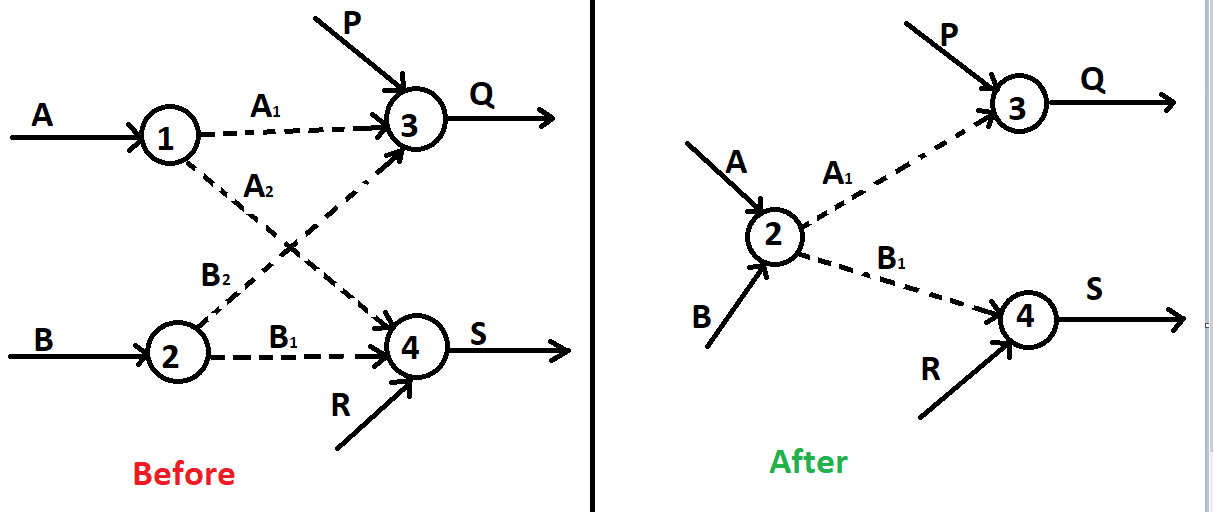
Here, A2 and B2 dummy activities are not required
Rule: 5
Do not repeat already implied logic.