5 Types of Sewer Pipe Joints
Following are the 5 common types of sewer joints:
1) Bell and Spigot Joints.
2) Collar Joints.
3) Flexible Joint.
4) Expansion Joint.
5) Flanged Joint.
1) Bell and Spigot joints
This joint is also known as socket and spigot joint. This type of joint is mainly used for cast iron pipes of all sizes and concrete pipes below 60 cm in diameter.
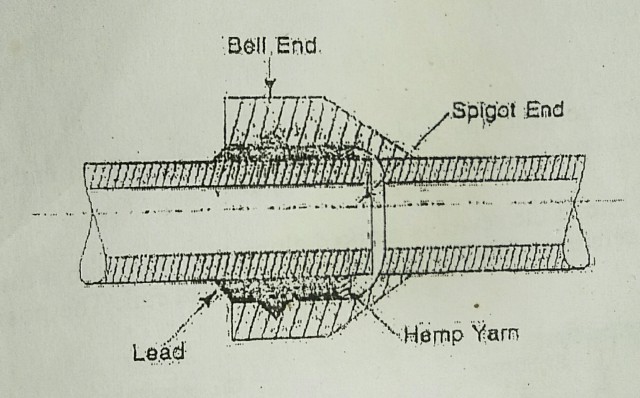
The pipes that are to be joined by this joint are made in such a way so that one end is enlarged arid the other end is normal. The enlarged end is called socket or bell and the normal end is called spigot. The spigot end is inserted into the bell end and the gap of the joint is filled up with molten lead or bitumen or cement mortar.
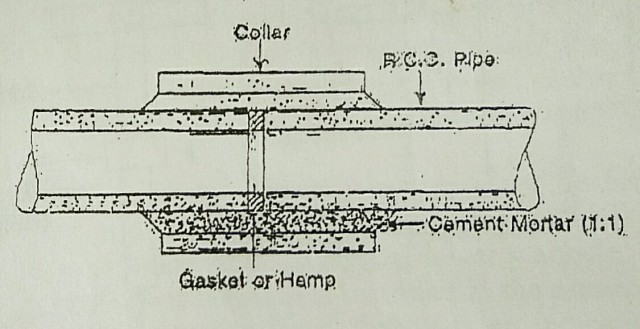
2) Collar joints
In this type of joint, the ends of the sewer are plain. Before joining, the pipes are brought face to face at the same level and a collar of slightly bigger diameter is placed over the joint. Then the annular space between the pipes and the collar is filled up with cement mortar (1:1). The collar joints are used for sewers of large diameter.
3) Flexible joint
This joint is used at such places where settlement is likely to occur after laying of the pipe. For this joint, one pipe has spigot end and another pipe has socket end. The spigot is fitted into the socket and bitumen is filled in the annular space formed between socket and spigot.
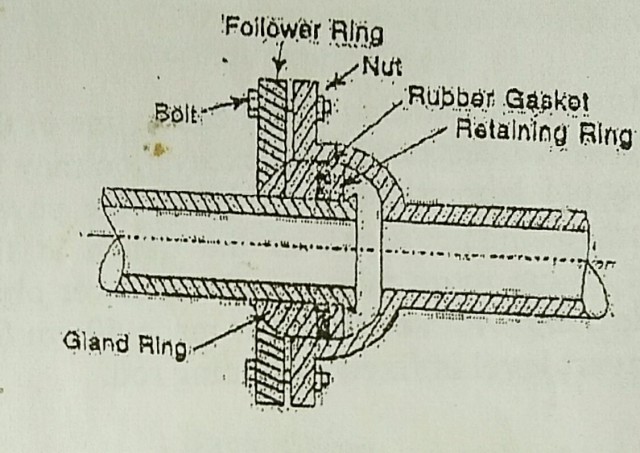
4) Expansion joint
This joint is adopted at places where pipes expand or contract due to variations in atmospheric temperature. Here the socket end is cast flanged and the spigot end is plain. A flanged ring and a rubber gasket are placed in position on the spigot end. Then the spigot end is inserted into the socket end nut and the bolts are tightened.
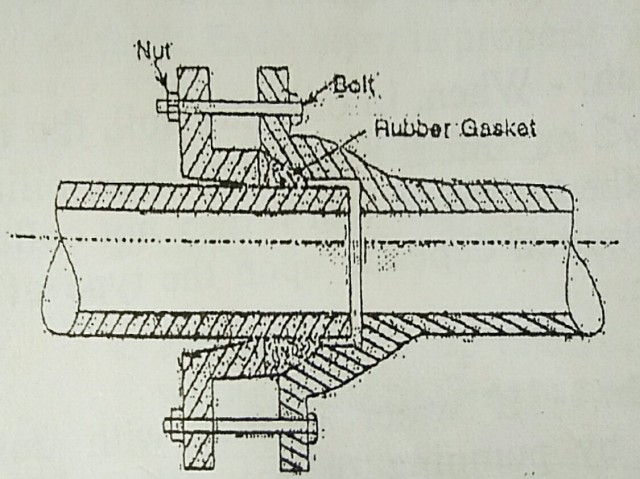
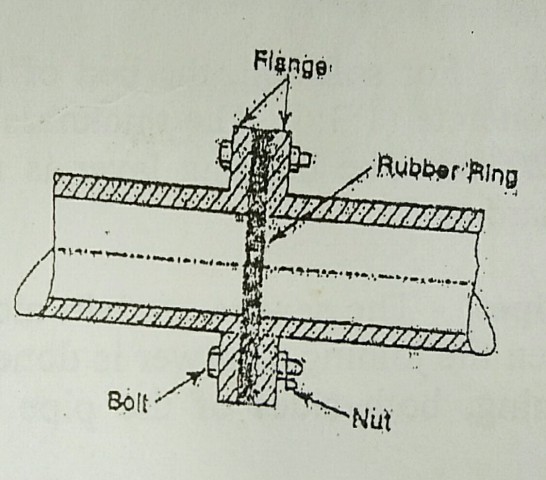
5) Flanged joint
This joint is mostly used for temporary work. The pipe used in this type of joint has flanges on both ends. While joining the pipes, a rubber gasket is inserted between the flanges and nut bolts are tightened.
Read Also:
Sewer Joint And Necessary Conditions For Making Sewer Pipe Joint