Laying Of Sewer Pipes
All the sewer pipes are generally laid starting from their outfall end towards their starting. The laying of new sewer pipes consists of the following 9 steps:
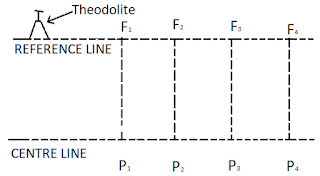
1. Marking Of The Alignment
The center line of the sewer is marked along the road with a theodolite and invert tap. It may be marked either by the reference line or with the help of the sight rail. The position of the manhole is also marked.
2. Excavation Of Trench
After marking the center line of the sewer, the excavation of the trench is started. The excavation may be carried out either by manual labor or by machines like power shovels, track excavators, etc.
The width of the trench at the bottom is generally kept 15 cm more than the dia of the sewer pipe. At the point of sewer joint, the width of the trench is made 60 cm for a length of 60 cm. The invert level is fixed by the boning rod.
3. Timbering Of The Trench
When, in ordinary soil, the depth of excavation is more than 2 m, timber bracing or sheet piling is provided on both sides of the trench so that it may not collapse. The extent of timbering required depends upon the type of soil and the depth of excavation.
4. Dewatering Of Trench
If water is met with during excavation, it is removed by pumping or any other suitable method.
5. Preparation Of Sub-grade
For soft soil, the bed of the sewer is prepared by plain concrete (1:3:6). The thickness of concrete varies from 15 to 20 cm. The bedding layer is not required in case of rocky or hard soil.
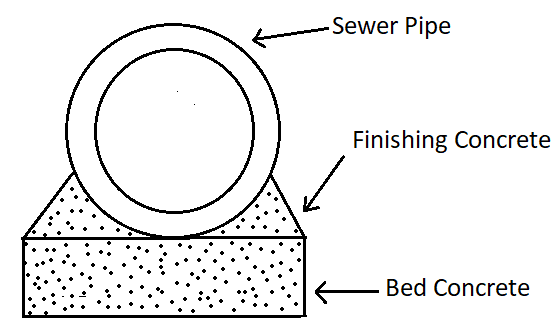
6. Laying And Joining Of Pipes
The sewers are laid along the trench very carefully. Then the joining of the sewer is done as per requirements. After joining, both sides of the pipe are finished with concrete.
7. Testing Of Leakage
The leakage in the pipe joints or any other points is tested by water test or air test…..Read more(Testing of leakage in the pipe joint -Air Test & Water Test).
8. Testing of Straightness Of Alignment And Obstruction
The straightness of the sewer pipe and the presence of any obstruction are tested by placing a mirror at one end of the sewer and a lamp at the other end. If the pipeline is straight, the full circle of light will be observed.
The presence of an obstruction in the pipe can also be tested by inserting a smooth ball at the upper end of the sewer. The dia of the ball is 13 mm less than the internal diameter of the sewer. If there is no obstruction inside the sewer, the ball shall roll down and reach the lower end of the sewer.
9. Back Filling
Lastly, the trenches are filled up with the excavated earth in layers about 15 cm thick. Each layer is properly watered and rammed.
Read Also:
Sewer Joint And Necessary Conditions For Making Sewer Pipe Joint
Separate Sewer System And Their Advantages & Disadvantages
7 Requirements of a Good Sewer Pipe