18 Different Component Parts of an Arch
An arch is a structure that is constructed over the opening of the windows, doors or cupboards, etc. The arch structure is also used in bridge construction. In ancient times, it was the most common structure used in any type of building. Arch may be circular, elliptical, or any other shape. It consists of wedge-shaped blocks of stone, bricks, etc. It may be made of steel or R.C.C. in case of bridge construction. In this article, I am going to share different component parts of an arch and also some technical terms used in arch construction.

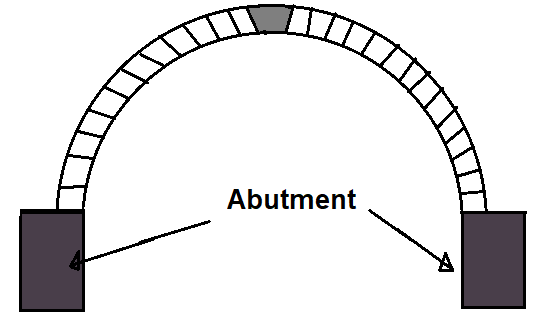
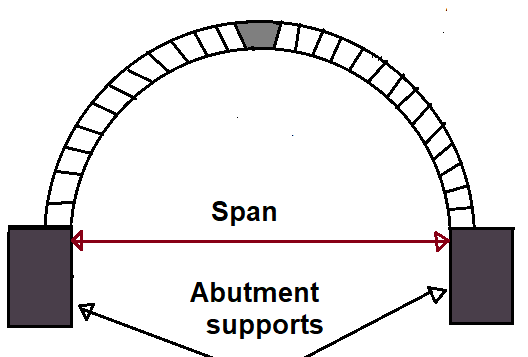
1. Abutment
The abutment is the end support of an arch. In other words, it is the end support of a span on which the arch rests. The abutment may be walls or columns in the case of buildings and retaining walls in the case of a bridge. An abutment should be designed in such a way that it can easily withstand arch thrust.
2. Piers
Piers is also a supporting member of an arch, but it is the intermediate supporting member. Piers are used when a series of arches is constructed.
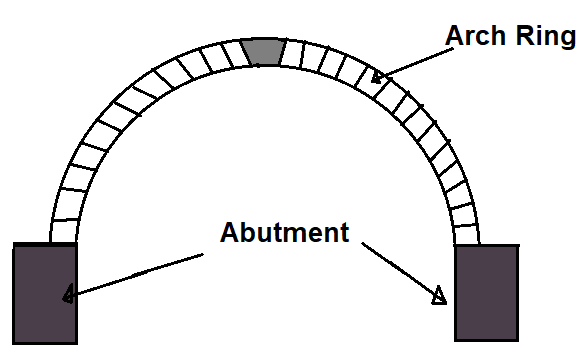
3. Arch ring
It is a course of wedge-shaped blocks, arranged in a curved form and supported on the abutments or piers.
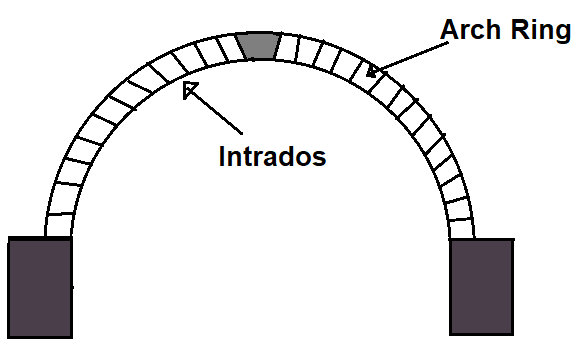
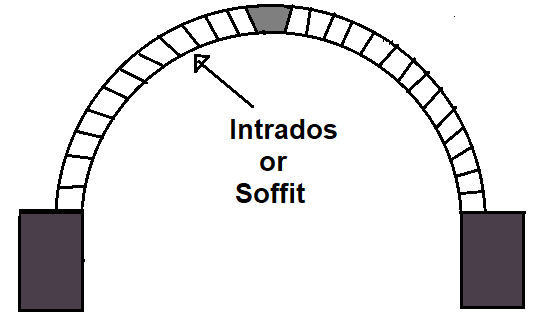
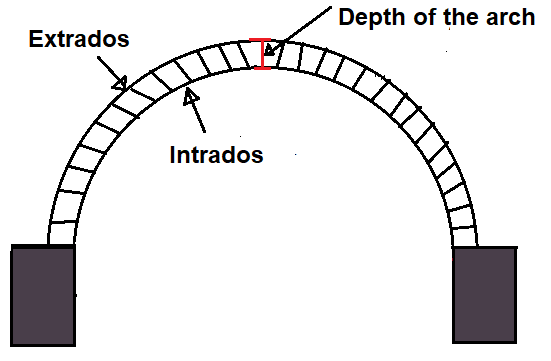
4. Intrados
This is the inner curved surface of the arch.
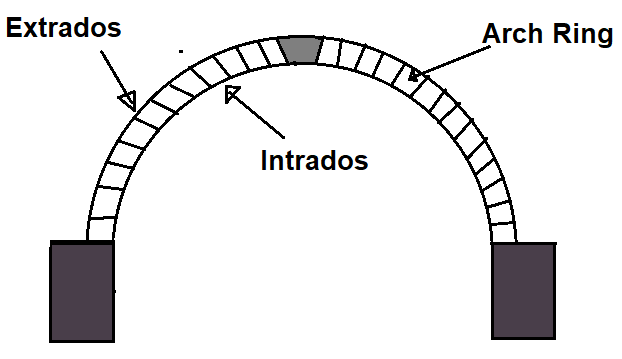
5. Extrados
This is the outer curved surface of the arch, it is also known as the back of the arch ring.
6. Soffit
The soffit is the bottom surface of the arch. Indrados and soffit terms are used to indicate the same thing.
7. Span of the Arch
The span of the arch is nothing but a clear horizontal distance between the supports.
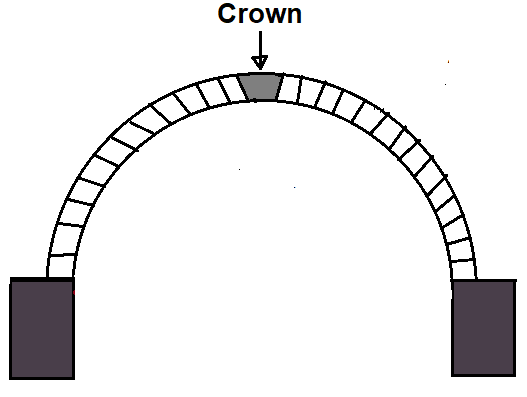
8. Crown
The Crown is the highest part of an arch. In other words, it is the height points of the extrados arch.
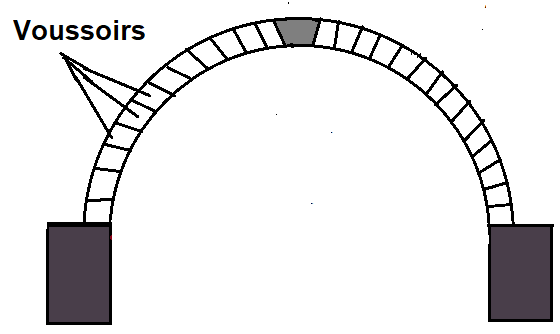
9. Voussoirs
Voussoirs are wedge-shaped units by which the arch ring is created. These block units may be of brick, stone, or plain cement concrete. Voussoirs are also called arch blocks.
10. KeyStone
Key stone is also a wedge-shaped block unit but it is larger than the voussoirs. This unit is placed at the highest point of the arch.
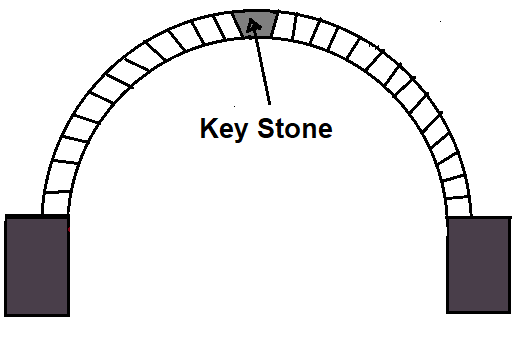
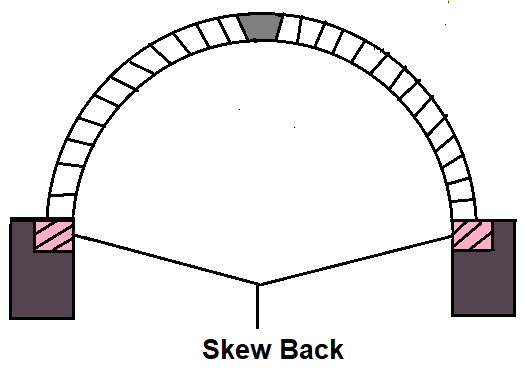
11. Skew Back
It is the splayed surface prepared on the top of an abutment or pier, to receive the arch. Arch work actually starts from skewback.
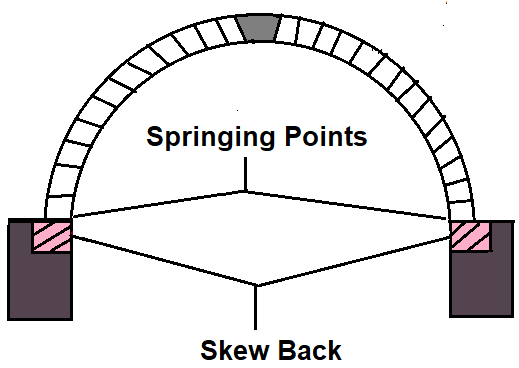
12. Springing Points
These are the points from where the curve of an arch starts. In other words, these are the points at which intrados and skew backs intersect.
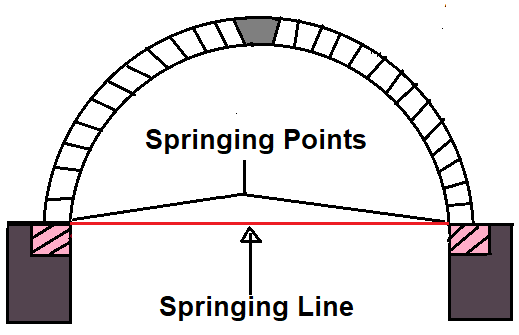
13. Springing Line
The springing line is nothing but the imaginary horizontal line joining the two springing points.
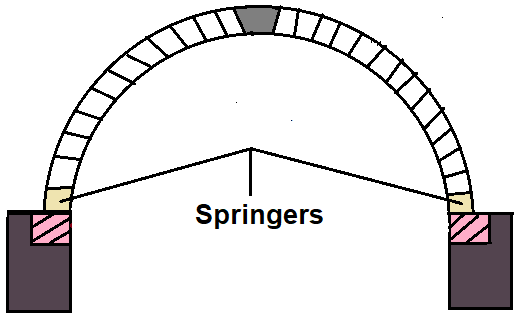
14. Springers
It is the first voussoir (or, beginning voussoir) at the springing level on either side of the arch.
15. Depth of the arch
It is the verticle distance between the intrados and extrados of an arch.
16. Haunch
If you imagine a line between crown and skewback, then the portion below the imagined line is known as Haunch.
17. Center of the arch
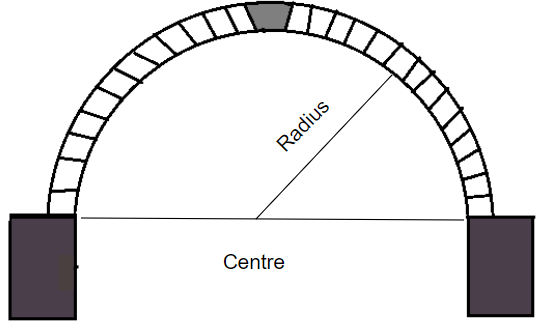
As its name suggests, it is the geometrical center of the curve of an arch.
18. Rise of the arch
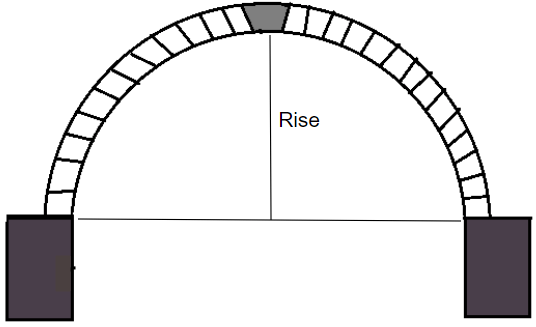
It is the perpendicular distance between the springing line and the highest point of the below curve(intrados) of the arch.
Read More: