Angle of Crossing in Railway
The angle which is formed between the gauge faces of the Vee is known as the crossing angle or angle of the railway crossing. Following are the three methods used to determine the angle of crossing in railway.
1. Right Angle or Cole’s Method
In this method, a right angle triangle is used to determine the angle of crossing.
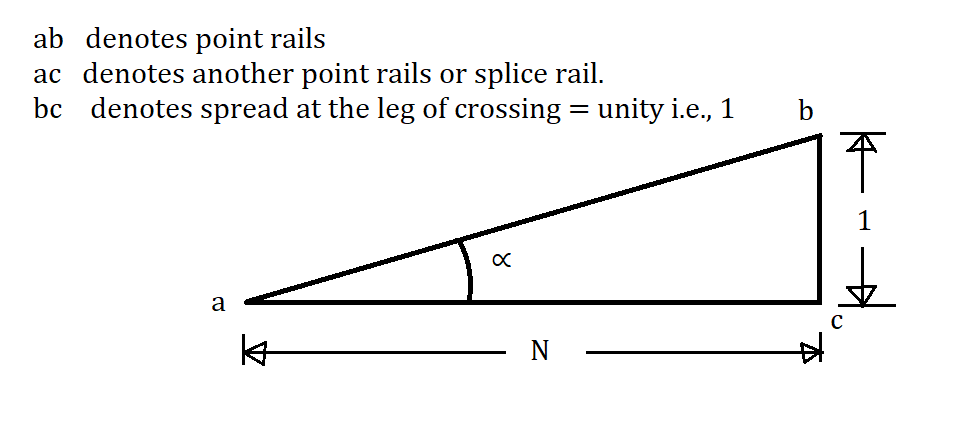
Notation:
- [latex] \alpha [/latex]= Angle of Crossing
- N = Crossing Number
From this Figure, we can write
[latex] \tan \alpha = \frac{1}{N} [/latex]
Or, [latex] \cot \alpha = N [/latex] …………(1.a)
Or, [latex] N = \cot \alpha [/latex] …………(1.b)
Equation (1.a) shows the angle of crossing.
Equation (1.b) shows the number of crossings.
Note: This is the standard method mostly adopted by the Indian Railways.
2. Centre Line Method
In this method, the measurement is taken along a line bisecting the crossing angle as shown in Fig.

Now,
[latex] \tan \frac{\alpha}{2} = \frac{\frac{1}{2}}{N} = \frac{1}{2N} [/latex]
Or, [latex] \cot \frac{\alpha}{2} = 2N [/latex] …………..(2.a)
Or, [latex] N = \frac{1}{2}.\cot \frac{\alpha}{2} [/latex] ……….(2.b)
Equation (2.a) shows the angle of crossing.
Equation (2.b) shows the number of crossings.
Note: This method is adopted in some countries like U.K. and U.S.A.
3. Isosceles Triangle Method
In this case, the measurement is taken along one side of the isosceles triangle as shown in fig.
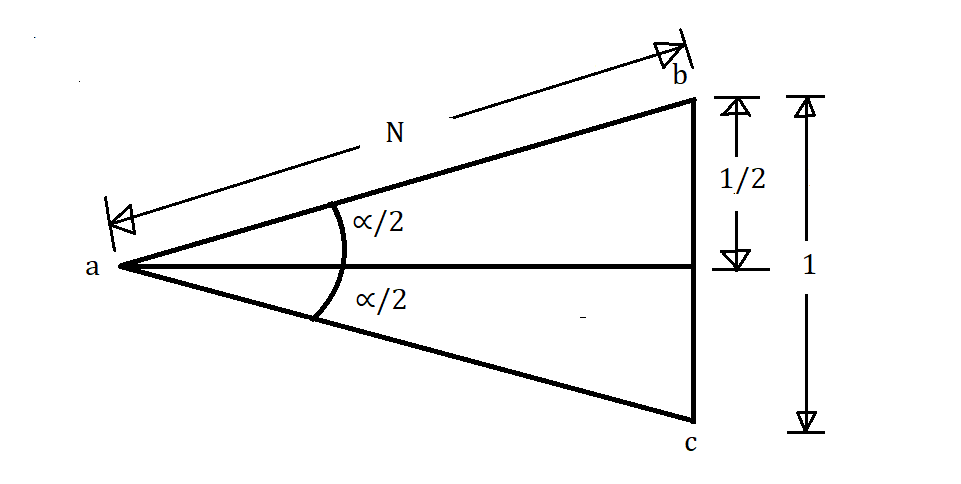
Then,
[latex] \sin \frac{\alpha}{2} = \frac{\frac{1}{2}}{N} = \frac{1}{2N} [/latex]
Or, [latex] cosec \frac{\alpha}{2} = 2N [/latex] …………..(3.a)
Or, [latex] N = \frac{1}{2}. cosec \frac{\alpha}{2} [/latex] ……….(3.b)
Equation (3.a) shows the angle of crossing.
Equation (3.b) shows the number of crossings.
Note: This method is implemented in the case of tramway layout.
More the angle of crossing lesser will be permissible speed and vice versa
Permissible Speed on Different Crossing
| Crossing | Different Gauge | ||
| B.G | M.G | N.G | |
| 1 in 8.5 | 16 km/h | 16 km/h | 16 km/h |
| 1 in 12 | 24 km/h | 22.5 km/h | 16 km/h |
Read More: