Different Types of Brick Cuts
There are several types of brick cuts that are generally created to fulfill the requirement for brick masonry work. In this article, I will show you all types of brick cuts that are usually used in brick masonry work.

1. CLOSER
It is nothing but a piece of bricks used to close up the bond at the end of the course. It is prepared by the worker with the edge of the trowel. In this case, the cut is always done along with the longitudinal edge. Broadly closer are divided into the following categories – king closer, queen closer, beveled closer, mitred closer.
2. QUEEN CLOSER
This is longitudinally cut, half-brick. These cut bricks are obtained by cutting a full brick longitudinally in two equal parts. The queen closer is ever used immediately after quoin header to obtain the break of vertical joints from the brick course immediately below this course.
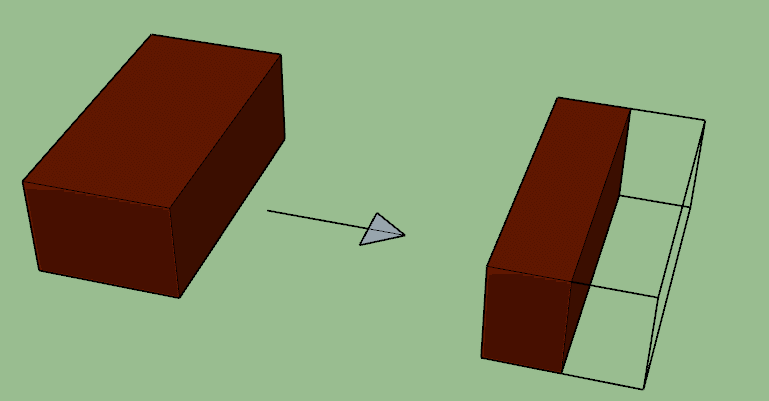
3. QUEEN CLOSER (QUARTER)
When the queen closer or half queen closer is further divided into two equal parts along its wide is called quarter closers.
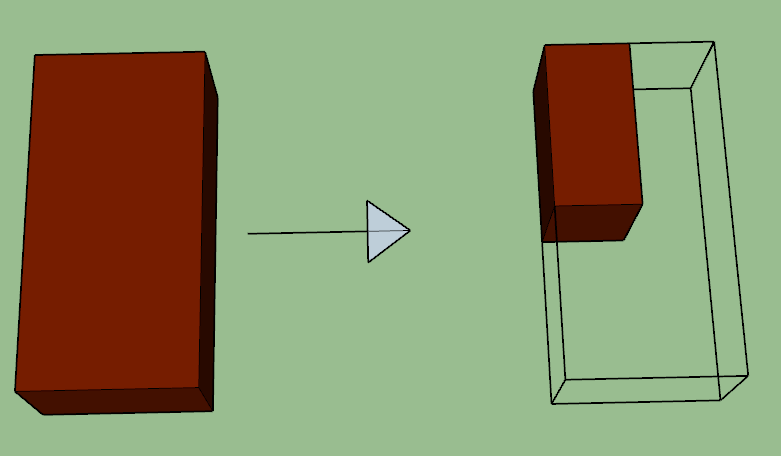
4. KING CLOSER
This piece of brick is obtained by cutting a triangular portion of the brick along the middle points of the length and width of the brick. It is mostly used near the door and window opening to get a proper arrangement of the mortar joints.
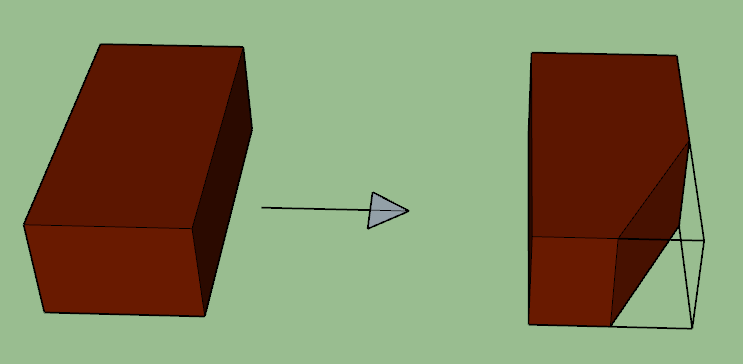
5. BEVELED CLOSER
It is another type of brick closer. Beveled closer is prepared by cutting a triangular portion of the brick in such a way that the cutting portion is started from a corner of the brick and ended at the middle portion of the other header face. This closer appears as the queen closer from one face but the full header from the other face. It is usually used for splayed brickwork, as in the case of jambs of doors and windows.
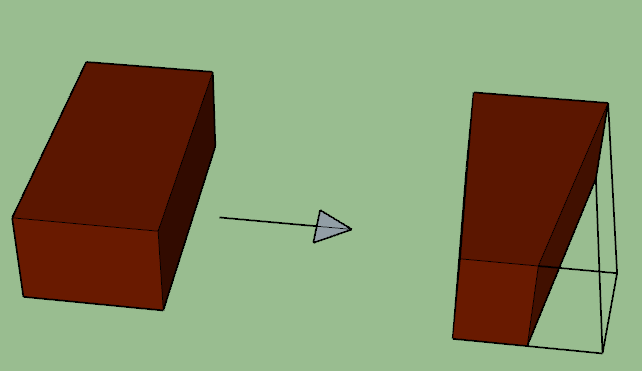
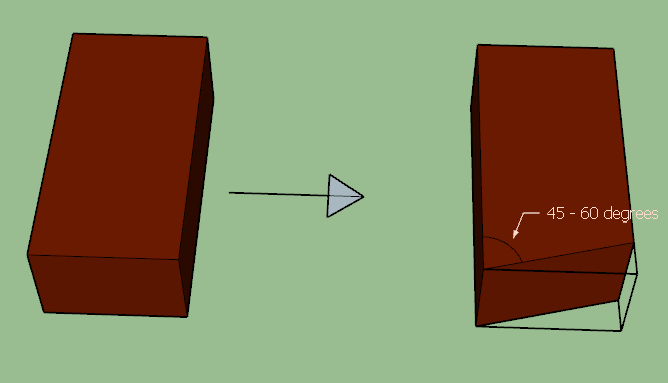
6. MITRED CLOSER
Mitred closer is obtained by cutting a triangular part of the brick in such a way that the cutting face is inclined at 45 to 60 degrees with a longer stretcher face of the brick. One longer face of this closer is smaller than its original length, whereas another longer face is intact.
7. BAT
It is a piece of a brick and is designed according to its length or we can say it is part of a brick named according to its length. Generally, bats are classified into three categories, they are Half bat, three-quarters bat, and beveled bat.
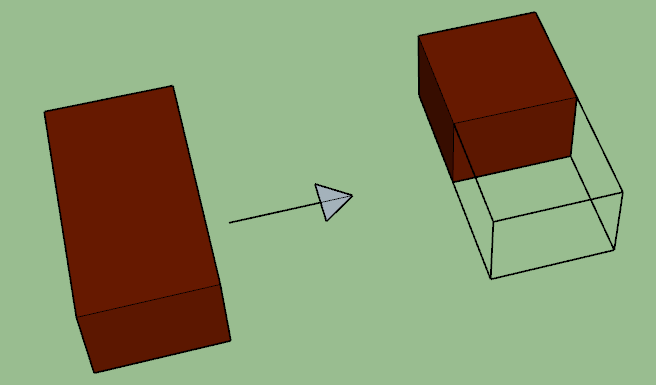
8. HALF BAT
Half bat – In simple words, when the brick length is Half then it is called Half bat. In other words, if the bat is Half brick in length, it is termed Half bat.
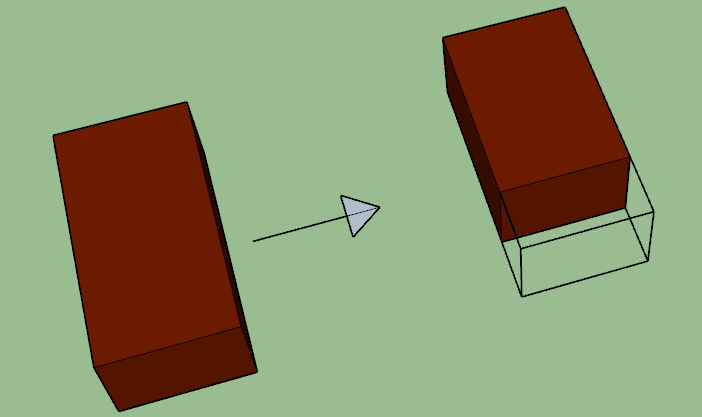
9. THREE-QUARTER BAT
If the bat is three-quarters of the brick length (i.e. 3/4), then it is called a three-quarter bat.
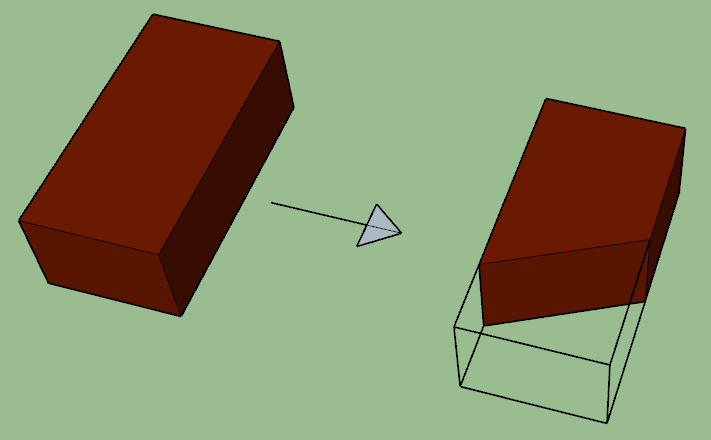
10. BEVELED BAT
If the bat is prepared as beveled in shape, then it is called a beveled bat.
11. BULLNOSE
When the brick is moulded or cut or dressed with a rounded angle, it is called bullnose. It is used in form of quoin. A brick with a double bullnose is called cownose brick.
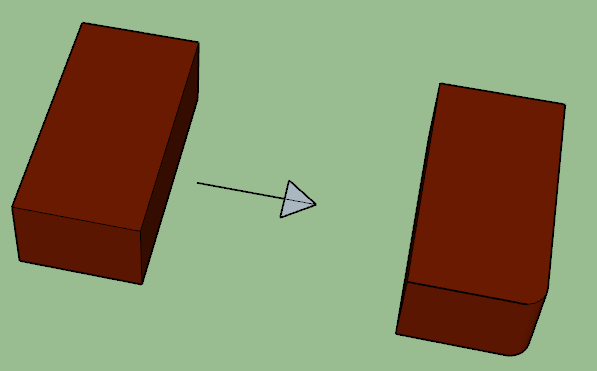
12. Squint quoin
Squint quoin is a piece of brick. It is obtained by moulding or cutting in such a way that in-plane angle rather than right angle is formed.
FAQs on Brick Cuts
What is the dimension of three quarter bat brick?
As the name suggests, three quarters that men’s 3 parts out of 4. So, the dimension of a ‘three-quarter bat brick’ is equal to the 3/4th fraction of a brick.
Read Also:
Characteristics of First Class Bricks