Kerbs
What is Kerbs?
Kerbs are the component of a city road. A kerb also termed as a curb is a vertical or sloping member provided along the edge of a pavement or Shoulder to give strength and protect the edge of the pavement.
The meaning of kerbs or curbs is a barrier or boundary. However, in highway engineering, it indicates the boundary between the pavement and shoulder or sometimes island or footpath or car parking space.

kerbs are generally constructed of cut stone or cement concrete slabs. The kerb and the road surface near the edge together from a side channel which carries rainwater that comes from the road surface.
4 Types of Kerbs
Kerb is the boundary between the pavement and shoulder or footpath. kerb may be divided into four groups based on their functions.

Following are the 4 types of kerbs are used in the roads:
(a) Low or Mountable Kerbs
This is also known as class I kerb. Its principal role is to control traffic to stay within its own lane. As the height of this form of kerb is low, it facilitates the driver to enter the area of the shoulder with less difficulty.
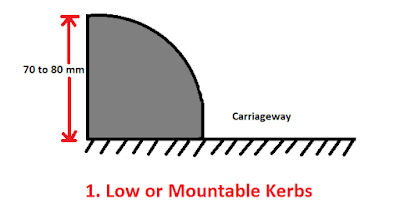
This type of kerb is also beneficial for the longitudinal drainage system. The height of this type of kerbs is 70 to 80 mm.
(b) Low-Speed Barrier or Urban Parking Kerb
This is also known as Class II kerb. It prevents encroachment of slow speed or parking vehicles to the footpath. However, with severe emergency vehicles, they can climb and be parked on footpath or shoulder.
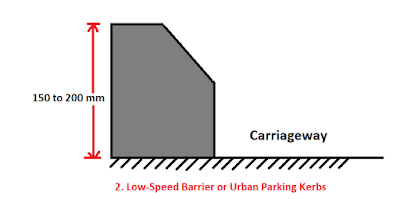
The height of this type of kerb is 150 to 200 mm with a batter of 25 mm to avoid the scraping of tyres.
3. High-Speed Barrier Kerbs
This is also known as Class III kerb. It is usually used in critical places such as bridges or mountain roads, This type of kerbs are 230 to 450 mm or more in height.

4. Submerged Kerbs
Submerged kerbs are provided in rural roads at pavement edges between the edge and shoulders. It is provided in the form of standing bricks or concrete blocks.

It offers lateral stability to the granular base course and flexible pavements.
What are the uses of road kerbs?
Curbs or kerbs are provided for the following purposes:
1. This prevents the vehicle from parking beside the road.
2. It acts as a boundary between the pavement and the footpath.
3. Kerbs provide structural support for the pavement.
4. It helps to overcome slipping risk of the vehicles.
5. It helps to reduce the number of accidents.
6. It is also used for drainage purposes.
Read Also:
5 Components of a City Road-Footpath, Kerbs, Pedestrian Crossing, Traffic lane, Median