Types of Rails
In railway engineering, there are 3 types of rails used in the construction of railway tracks which are discussed below:
- Double Headed Rails.
- Bull Headed Rails.
- Flat Footed Rails.
Above three Types of rails are described below in detail:
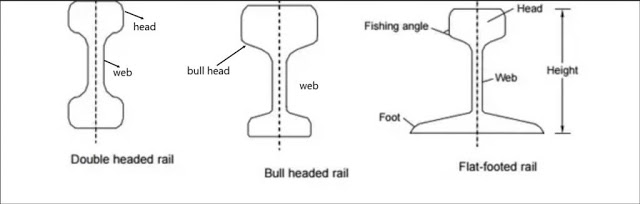
1. Double Headed Rails
The rail sections, having their head and foot of same dimensions, are known as double headed or Dumb-bell rails. These rails have less strength and stiffness as compared to flat footed rails. These rails are not used nowadays on Indian Railway.
2. Bull Headed Rails (B.H Rails)
The rail section, having the head a little thicker and stronger(Bull size) than the lower part is known as Bull headed rails. These rails have less strength and stiffness as compared to flat footed rails. Bull headed rails are generally used for constructing points and crossings.
Advantages of Bull Headed Rails
1. They keep better alignment and give a more solid and smoother track.
2. The rails can be easily removed and replaced quickly. Hence renewal of the track is easy.
3. The heavy chair with a large bearing on sleepers gives longer life to the wooden sleepers and greater stability to the track.
4. These rails facilitate easy manufacturing of points and crossings.
Disadvantages of Bull Headed Rails
1. They require costly fastenings.
2. They have less strength and stiffness.
3. They require heavy maintenance costs.
3. Flat Footed Rails(F.F. Rails)
The rail sections, having a flat foot, are known as flat-footed rails. These rails have more strength and stiffness as compared to Double Headed Rails & Bull Headed Rails. Flat footed rails are most commonly used in India.
Advantages of Flat Footed Rails
1. These rails have more strength and stiffness.
2. Fitting of rails with sleepers is simpler so they can be easily laid and re-laid.
3. No chairs and keys are required as in case B.H. rails.
4. Maintenance of points and crossings made with these rails is easy.
5. They give better stability and longer life to the track and reduces maintenance cost.
6. These rails are less costly than other types of rails.
7. These rails require less number of fastenings.
Disadvantages of Flat Footed Rails
1. The fitting gets loosened more frequently.
2. The straightening of bent rails, replacing of rails, and de-hogging of battered rails are difficult.
3. These rails sink into the wooden sleepers under heavy trainloads. Hence they require a bearing plate to overcome this problem.
4. Manufacturing of points and crossing with these rails is difficult.
FAQs
How many types of rail sections are there?
There are three types of rail sections, they are 1. Double Headed Rail, 2. Bull Headed Rail and 3. Flat-Footed Rail section.
What is the meaning of the 25R, 35R, 45R, and 55R rail sections?
25R, 35R, 45R, and 55R means that the weight of the rail section per meter length is 25 Kg, 35 Kg, 45 Kg, and 55 Kg respectively.
Read More: