Bulking Of Sand
The volume of fine aggregates may be increased by 1% to 25 % due to the presence of moisture in it. This property of the increase in the volume of fine aggregate i. e sand due to moisture is called bulking of sand.
Causes of Bulking Of Sand
Bulking occurs due to the formation of a thin film of water around the sand particles. When the sand is moistened, free moisture forms a film around every particle which tends to keep the particles away from one another & thus causes bulking of sand.
Factors Which Affecting The Bulking of Sand
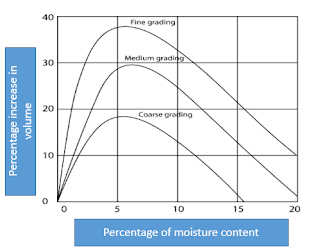
The extent of bulking depends upon the
- The fineness of sand. Finer sands bulk considerably more than coarse sand.
- Moisture present in the sand. It has been observed that the addition of 5% to 6% of moisture may increase the volume of dry sand by 18% to 38 %. If the percentage of moisture content is beyond 10%, the increase in bulk of sand starts decreasing. When the sand is completely saturated, its volume becomes equal to that of dry sand.
Thus, while grading aggregates, the bulking effect of sand should be considered and the proportioning should be corrected accordingly.
If no allowance is made for bulking, the mix will be richer than specified. This also causes the deficiency of sand in a mix which increases the chances of segregation and honeycombing of concrete. The yield of concrete will also be reduced.
Bulk Density of Aggregate
The bulk density of an aggregate may be defined as the mass of the material in a given volume. It is normally expressed in kg/litre. It depends on low densely the aggregate is packed.
Factors Affecting The Bulk Density
Factors affecting the bulk density are the
- Particle size
- Particle Shape
- The grading of the aggregate
- Moisture content
Read Also: